By Rachael Pfenninger, Director of Strategic Execution, AMBA
In AMBA’s recent 2021 Business Forecast Report, mold manufacturers indicated that, on average, healthcare costs accounted for 20% of total company expenditures. This is shockingly high when compared to recent data from the National Compensation Survey (NCS) program, which reported that healthcare costs constituted an average of only 8% of total compensation for civilian workers in March 2020.1 It also indicated that for the mold manufacturing community, mitigating healthcare costs that continue to rise year-over-year is becoming an urgent priority, particularly in an industry recovering from months of COVID-19-related environmental and economic challenges.
To address this area of interest and provide urgently needed insight and guidance, AMBA again has benchmarked the costs and plan offerings of mold manufacturers in its second annual 2021 Health and Benefits Report. To provide additional perspective, the AMBA benchmarking team worked alongside the Manufacturers Association for Plastics Processors (MAPP) and the Association of Rubber Products Manufacturers (ARPM) to expand the report scope, which is inclusive of year-over-year increases, cost mitigation strategies and more.
Manufacturers Continue to Battle Rising Healthcare Costs
According to numbers reported during this benchmarking effort, which collected data from more than 200 companies and represented nearly 27,000 full-time employees, eight out of 10 executives indicated that their health insurance rates increased in 2020. More alarming is that, while 38% of these executives reported a rise that ranged from 6% to more than 30%, 47% anticipate a similar rise in 2021.
With an average enrollment of 70%, the total average annual company cost to provide medical benefits (inclusive of all three industries) equaled $727,000, with an average cost per participating employee per year (PEPY) of $10,143.
While the perspective of all surveyed manufacturers is helpful to understand, it is important to note that the mold manufacturers segment only averaged an annual average cost of $384,000 (a slight decrease from 2020 data). The average cost per PEPY also differed significantly from the overall report results. While the average cost PEPY in this year’s report equaled $10,143, surveyed mold manufacturers continue to pay approximately $11,150 PEPY, equal to 10% more than the average manufacturer surveyed. A deeper dive into the specific data for mold builders surveyed in this report revealed that this incremental cost largely can be attributed to the contract type as more than eight out of 10 executives use “fully insured” health plans, which have higher costs due to no sharing of risk between plan sponsors and plan providers (aka insurance companies).
Ripple Effects of Workforce Representation
 One significant factor that may contribute to rising healthcare costs for many manufacturers (and mold builders, in particular) is the trend data associated with employee representation by age group. For instance, as the workforce representation rose for groups of employees aged 18 to 30, 31 to 40, 41 to 45 and 46 to 50, average cost per employee steadily dropped. However, as the percentage of employees above the age of 50 rose, the trend began to reverse – for companies where a larger percentage of the workforce was aged 51+, the average cost of healthcare per employee steadily rose. This trend held true for ages 51 to 55, 56 to 60, 60 to 65 and 66+.
One significant factor that may contribute to rising healthcare costs for many manufacturers (and mold builders, in particular) is the trend data associated with employee representation by age group. For instance, as the workforce representation rose for groups of employees aged 18 to 30, 31 to 40, 41 to 45 and 46 to 50, average cost per employee steadily dropped. However, as the percentage of employees above the age of 50 rose, the trend began to reverse – for companies where a larger percentage of the workforce was aged 51+, the average cost of healthcare per employee steadily rose. This trend held true for ages 51 to 55, 56 to 60, 60 to 65 and 66+.
Contributing Factors to Healthcare Costs
 To combat escalating changes in healthcare costs, executives are exploring a wide variety of options; however, 50% of the survey respondents have no real strategy for dealing with the variables affecting their most inflationary expenditures. In fact, the majority of the tactics being used today are ones that have been used and reused by employers for the last two decades, and truly do not address the core issues that impact employers’ ability to provide insurance benefits to employees over the long-term.
To combat escalating changes in healthcare costs, executives are exploring a wide variety of options; however, 50% of the survey respondents have no real strategy for dealing with the variables affecting their most inflationary expenditures. In fact, the majority of the tactics being used today are ones that have been used and reused by employers for the last two decades, and truly do not address the core issues that impact employers’ ability to provide insurance benefits to employees over the long-term.
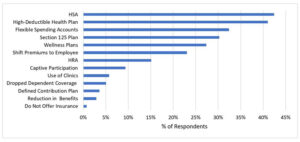
Currently, the most popular tactic – used by 42% of executives – is the use of Health Savings Accounts (HSA) in conjunction with the utilization of high-deductible health plans. Other tactics being implemented to offset rising costs include the use of flexible spending accounts (used by 32%), Section 125 Plans (used by 30%), wellness plans (used by 27%) and dropping dependent coverage (used by 5% of the surveyed population).
Unfortunately, nearly one in four executives is cost-shifting premiums to employees. In other words, leaders are moving more of the expense of insurance to the employment base – an approach that is estimated to negatively impact employee retention as the battle for talent continues to be the number one challenge for US businesses.
Key Strategic Initiatives Address Core Issues
This report does reveal that a small segment of organizational leaders in the mold building sector are using true strategies to insulate themselves against health insurance premium escalation. For example, 4.6% of the surveyed population now are using captive funding arrangements to buffer themselves against market fluxuations. Although insurance captives have been in use for decades, it is very importrant to note that nearly every insurance captive operates differently. However, a basic princple of insurance captives is to control the insurance dollars and to either eliminate or reduce the opportunity for insurance companies to make profits and recapture profits on the dollars spent.
The second strategy being used is the use of onsite and nearsite clinics. This concept is contrary to most insurance business models, providing free medical care and free commonly used generic medication to employees. The reason the use of clinics is growing in popularity is that the model reduces the use of highly marked-up services and prescription drugs and makes it easier and more affordable for people to be proactive in their own personal care.
Finally, one notable area of interest in this year’s report is that although only 12.5% of respondents in the mold building community – one in eight – indicated that they are engaging in wellness plan implementation, this is in stark contrast to the 27% of all surveyed manufacturers who are exploring this strategy. For any mold manufacturer not considering wellness plan implementation, this strategy could be a potential competitive advantage in 2021 and beyond – particularly because, according to the Society for Human Resource Management, more employers than ever are identifying wellness plan implementation as a form of cost mitigation when it comes to healthcare costs. In fact, as much as 70% of healthcare spending can be attributed to behavioral and lifestyle choices, which has led employers to provide continually robust health improvement opportunities.2
Ultimately, education provided to employees on how to use their health plan benefits, early detection, wellness and efforts to address the root cause of health issues can reduce long-term cost significantly. If employers continue to implement met hods that address these key areas, they will be able to mitigate their current costs and address potentially catastrophic issues in the future.
References
1.https:/www.bls.gov/ncs/ebs/factsheet/medical-care- premiums-in-the-united-states.htm
2.https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/toolkits/pages/managinghealthcarecosts.aspx
The AMBA 2021 Health and Benefits Report covers a vast array of topics, including significant details on health insurance, the process of managing insurance, ancillary insurance benefits, prescriptions drugs, 401K plans and more. Access the full report at AMBA.org.


